 Small articles may be galvanized by a variation on the standard hot dip galvanizing process and is known as ‘Centrifuge (or spin)
Small articles may be galvanized by a variation on the standard hot dip galvanizing process and is known as ‘Centrifuge (or spin)
Galvanizing’.
In centrifuge galvanizing the work follows the same process route as for larger articles except the items are loaded into a basket which is spun at high speed immediately after removal from the molten zinc.
This removes surplus zinc and improves the uniform distribution of the zinc coating, while preventing pieces from sticking together. Work is normally quenched immediately after centrifuging.
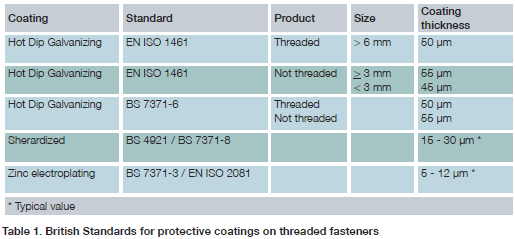
Protecting threads when galvanizing
As a general rule, bolts down to M8 threads can be readily galvanized and threaded components up to 2m long have been processed. Special arrangements might be made to galvanize threaded components outside of this range.For hot dip galvanized bolts and nuts, it is normal for standard bolts from stock to be galvanized; the nuts are galvanized as blanks and then tapped up to 0.4 mm oversize with the threads lightly oiled. When assembled the nut thread is protected by contact with the coating on the bolt.
Galvanized bolts and nuts can be readily unfastened even after many years of service.
Other fabricated small components
A wide variety of small components can be galvanized. Typical examples might include clamps, hinges, hasps and clips. The materials used and the design of the component must be suitable for hot dip galvanizing and advice is available from Galvanizers Association to ensure optimum design of components.

